NIO Channel类图Overview
Channel
Channel
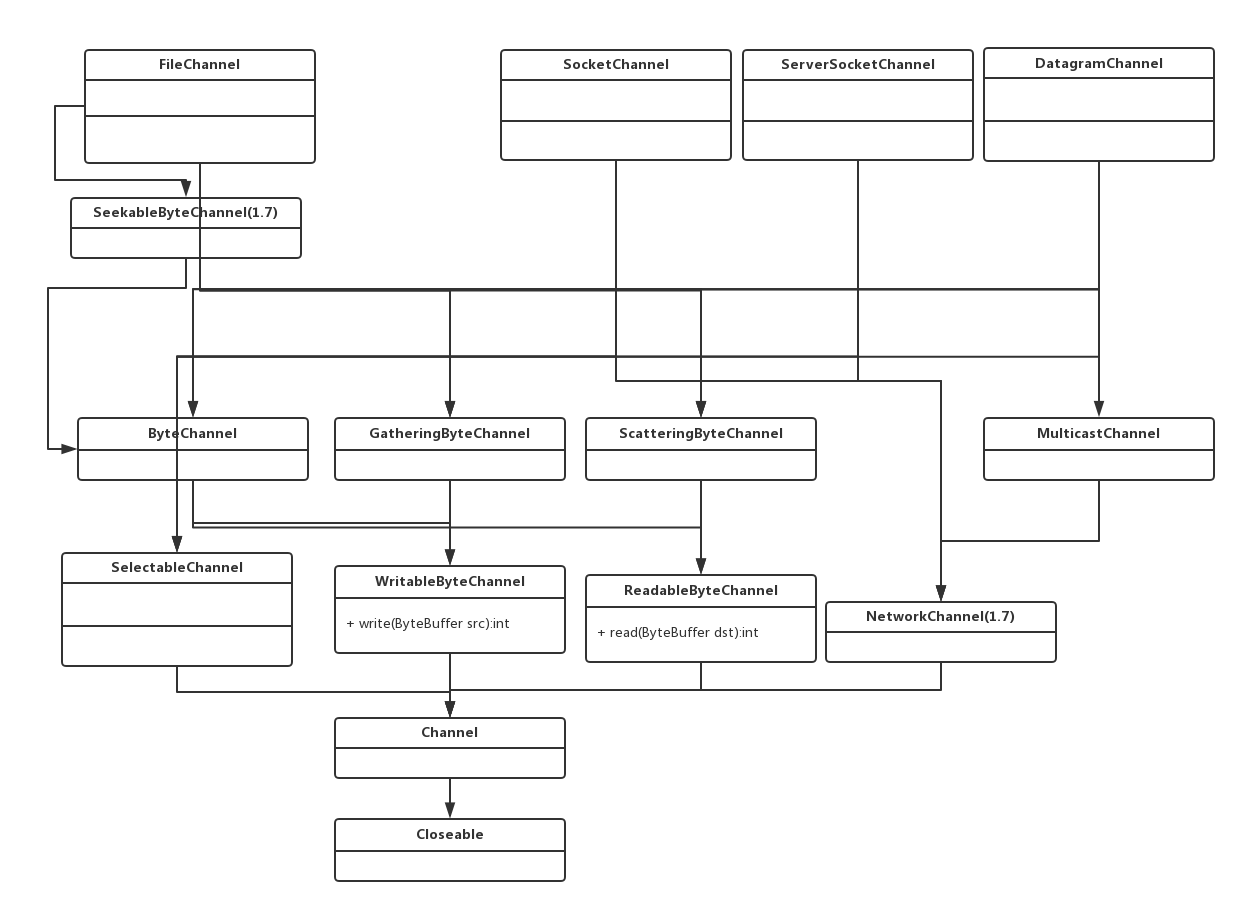
由上图可以看出,所有的Channel相关实现类最底层都实现了java.nio.channels.Channel接口,代码如下
public interface Channel extends Closeable {
public boolean isOpen();
public void close() throws IOException;
}Channel接口只提供了方法的定义。并没有具体的实现,而具体的通道实现使用操作系统的本地代码,所以不同操作系统的Channel实现会有很大的区别,但达到了最大限度的提高IO效率。
Readable和Writable
对于Channel,JDK定义了两种操作权限,一种是读权限(ReadableByteChannel),一种是写权限(WritableByteChannel),对应操作系统级别的读写权限,而所有的实现都是面向字节的操作,因为操作系统级别的IO操作都是字节级别的实现。
public interface ReadableByteChannel extends Channel {
public int read(ByteBuffer dst) throws IOException;
}public interface WritableByteChannel extends Channel {
public int write(ByteBuffer src) throws IOException;
}Scatter和Gather
针对ReadableByteChannel和WritableByteChannel只能针对单个ByteBuffer对象进行读写操作的缺点,JDK还扩展出了ScatteringByteChannel和GatheringByteChannel分别针对批量的读和写操作。Scatter/Gather可以在多个缓冲区上实现一个IO操作。大多数现代操作系统都支持本地矢量I/O(native vectored I/O)。当在一个通道上请求一个Scatter/Gather操作时,该请求会被翻译为适当的本地调用来直接填充或抽取缓冲区。
public interface ScatteringByteChannel extends ReadableByteChannel {
public long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts, int offset, int length)
throws IOException;
public long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts) throws IOException;
}public interface GatheringByteChannel extends WritableByteChannel {
public long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs, int offset, int length)
throws IOException;
public long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) throws IOException;
}FileChannel
针对FileChannel的打开,JDK有三种实现如下:
| RandomAccessFile.getChannel() | ReadableByteChannel, WritableByteChannel |
| FileInputStream.getChannel() | ReadableByteChannel |
| FileOutputStream.getChannel() | WritableByteChannel |
input1.txt
HelloWorld!RandomAccessFileTest
package com.freud.nio;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/**
* @author Freud
*/
public class RandomAccessFileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String file1 = "file/input1.txt";
String file2 = "file/input2.txt";
String file3 = "file/input3.txt";
RandomAccessFileTest test = new RandomAccessFileTest();
test.transforTo(file1, file2);
test.transforFrom(file2, file3);
}
public void transforTo(String src, String dest) throws Exception {
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File(src));
FileChannel channelFrom = is.getChannel();
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest));
FileChannel channelTo = os.getChannel();
channelFrom.transferTo(0, channelFrom.size(), channelTo);
channelFrom.close();
channelTo.close();
os.close();
is.close();
}
public void transforFrom(String src, String dest) throws Exception {
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File(src));
FileChannel channelFrom = is.getChannel();
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest));
FileChannel channelTo = os.getChannel();
channelTo.transferFrom(channelFrom, 0, channelFrom.size());
channelFrom.close();
channelTo.close();
os.close();
is.close();
}
}其他常用方法
| position() | 获取当前游标位置 |
| position(long newPosition) | 设置游标位置 |
| truncate(long size) | 截取文件,指定长度后的内容将被删除 |
| force(boolean metaData) | 将通道中尚未写入磁盘的数据强制写到磁盘上 |
SocketChannel
package com.freud.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
/**
* @author Freud
*/
public class SocketChannelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置是否为阻塞式Socket IO,如果非阻塞,则connet(),read(),write()方法都将为异步
// 本示例为阻塞模式,非阻塞模式将在Selector一章介绍
channel.configureBlocking(true);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 7794));
System.out.println("Connection building up.");
while (!channel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.print(".");
}
System.out.println();
// 发送Socket请求
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloWorld".getBytes()));
channel.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println("Client Request sended.");
ByteBuffer response = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
System.out.print(">>>");
// 解析返回的response
while (channel.read(response) != -1) {
response.flip();
while (response.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) response.get());
}
response.clear();
}
channel.shutdownInput();
System.out.println("\r\nFinished read from server.");
channel.close();
}
}ServerSocketChannel
package com.freud.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
/**
* @author Freud
*/
public class ServerSocketChannelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置是否为阻塞式Socket IO,如果非阻塞,则connet(),read(),write()方法都将为异步
// 本示例为阻塞模式,非阻塞模式将在Selector一章介绍
serverChannel.configureBlocking(true);
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(7794));
int count = 0;
// 循环接收所有Client的请求
while (true) {
try {
// 获取到Client的请求
SocketChannel channel = serverChannel.accept();
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
"Connection [{0}] build up.", count++));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
System.out.print(">>>");
// 解析请求内容
while (channel.read(buffer) != -1) {
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print((char) buffer.get());
}
buffer.clear();
}
channel.shutdownInput();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Finished read from Client.");
// 回写Response到Client
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloWorldResponse".getBytes()));
channel.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println("Finished write response to Client.");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}DatagramChannel
DatagramChannelServerTest
package com.freud.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
/**
* @author Freud
*/
public class DatagramChannelServerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 设置UDP Server相关信息,并启动Server
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open();
// 设置是否为阻塞式IO,如果非阻塞,则connet(),receive(),read(),write()方法都将为异步
// 本示例为阻塞模式,非阻塞模式将在Selector一章介绍
channel.configureBlocking(true);
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(7795));
while (true) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
// 接收UDP消息
SocketAddress address = channel.receive(buffer);
buffer.flip();
// 解析接收到的UDP消息
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.limit()];
int i = 0;
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
bytes[i] = buffer.get();
i++;
}
System.out
.println(MessageFormat.format(
"From client[{0}] value [{1}]", address,
new String(bytes)));
// 向发送UDP的地址发送Response消息。模拟TCP的有链接模式。
channel.send(ByteBuffer.wrap("Hello I am response.".getBytes()),
address);
System.out.println("Finished send the response.");
}
}
}DatagramChannelClientTest
package com.freud.nio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
/**
* @author Freud
*/
public class DatagramChannelClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 建立UDP连接
DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open();
// 设置是否为阻塞式IO,如果非阻塞,则connet(),receive(),read(),write()方法都将为异步
// 本示例为阻塞模式,非阻塞模式将在Selector一章介绍
channel.configureBlocking(true);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 7795));
// 发送UDP数据
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("Hi I am request................."
.getBytes()));
System.out.println("Finished send the request.");
// 接收UDP数据
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
// 解析接收到的UDP数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.limit()];
int i = 0;
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
bytes[i] = buffer.get();
i++;
}
System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
"Received the server side response [{0}]", new String(bytes)));
}
}参考资料
JAVA-NIO(英文版) - Ron Hitchens
JAVA-NIO(中文版) - Ron Hitchens(著) 裴小星(译)
Java nio tutorial : http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/index.html
并发编程网:Java NIO系列教程-中文翻译版 : http://ifeve.com/overview/