Pipe
概述
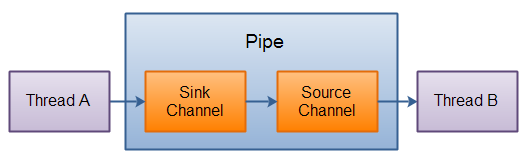
Java NIO Pipe是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。在多线程编程中除了wait(), notify(), notifyAll()等,增加了一种新的线程间通讯方式。Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。如下图示例,数据通过Thread A 写入 sink通道,然后通过Thread B 读取source通道获得数据。
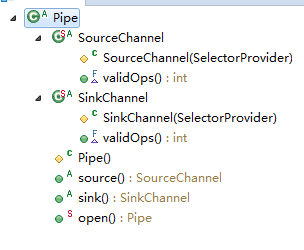
类结构
打开通道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();写入数据
重载方法有三个,与其他普通的Channel操作相同。分别是写入单个ByteBuffer,写入多个ByteBuffer,和指定长度写入多个ByteBuffer。
pipe.sink().write();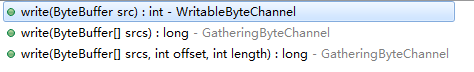
读取数据
重载方法有三个,与其他普通的Channel操作相同。分别是读入单个ByteBuffer,读入多个ByteBuffer,和指定长度读入多个ByteBuffer。
pipe.source().read();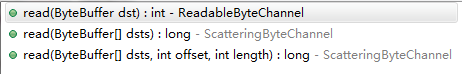
Demo
package com.freud.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Pipe;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* * @author Freud
*/
public class PipTest implements Runnable {
private Pipe pipe;
public PipTest(Pipe pipe) {
this.pipe = pipe;
}
public void run() {
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (pipe.source().read(buffer) >= 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.limit()];
for (int i = 0; buffer.hasRemaining(); i++) {
bytes[i] = buffer.get();
}
buffer.clear();
System.out.println("Input : " + new String(bytes));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
new Thread(new PipTest(pipe)).start();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
while (true) {
String input = scanner.next();
pipe.sink().write(ByteBuffer.wrap(input.getBytes()));
}
} finally {
scanner.close();
}
}
}参考资料
JAVA-NIO(英文版) - Ron Hitchens
JAVA-NIO(中文版) - Ron Hitchens(著) 裴小星(译)
Java nio tutorial : http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/index.html
并发编程网:Java NIO系列教程-中文翻译版 : http://ifeve.com/overview/